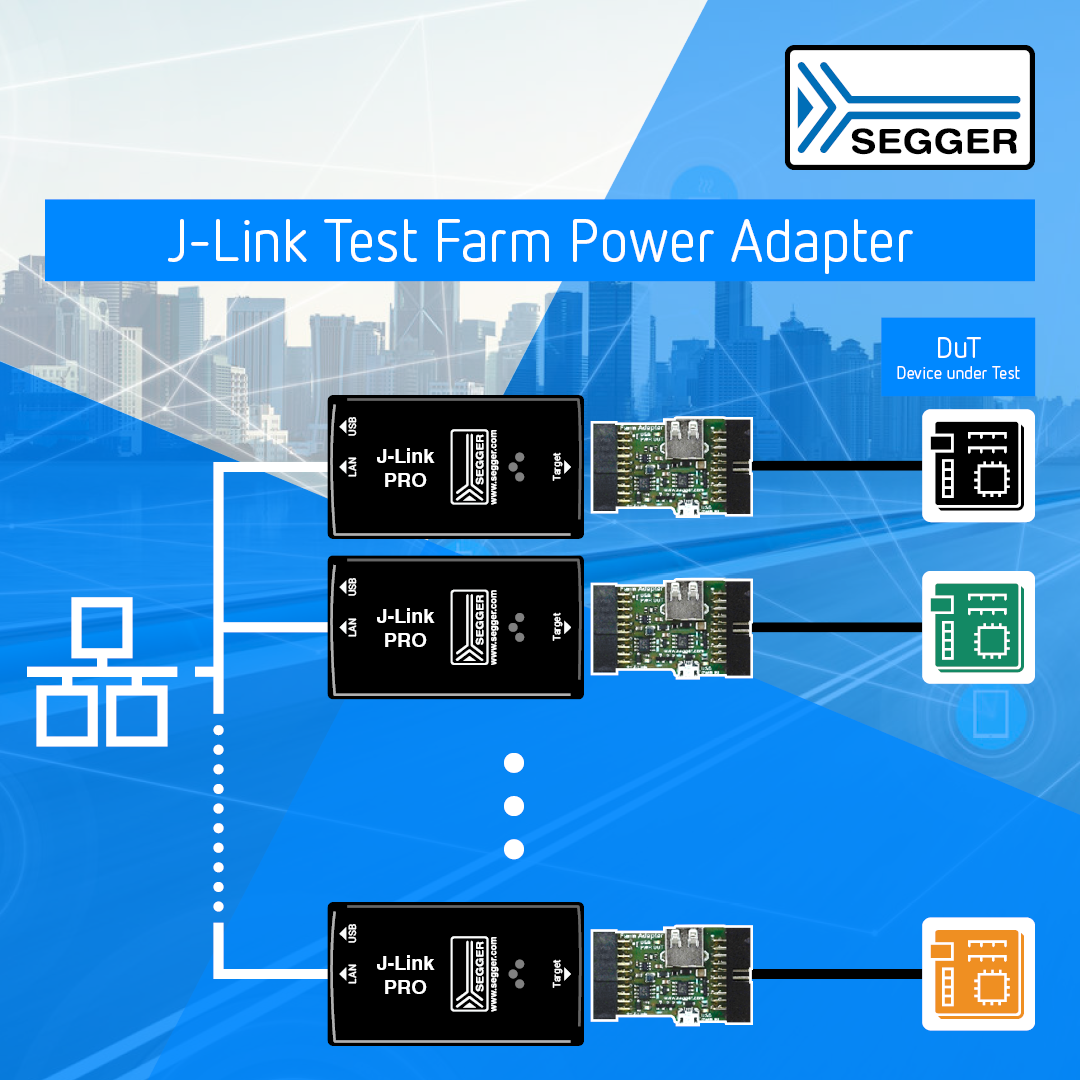
The Test Farm Power Adapter enables power that is supplied to a target through a USB connector to be switched on and off remotely using J-Link software. Since the debug signals are maintained, it can be used along with Ethernet featured debug probes like the J-Link PRO to build test farms.

What is a Test Farm
In terms of embedded systems, a Test Farm (or “board farm” or “device farm”) consists of a number of nodes (such as evaluation boards, prototype boards, production boards, finished products, etc.) connected to a network via debug probes, making them remotely accessible to testers or developers.
It is a very efficient way to share access to hardware that is in limited supply among a number of users. Additionally, automated build systems can run tests on the same standard setup, which is ideal for regression testing, continuous integration, compiler tests, and more.
The benefits of a test farm and how to build one
Find out more about test farms, including how to build a J-Link test farm with the J-Link Test Farm Power Adapter, on our Test Farm wiki page.
Use Cases
There is a large amount of use cases in almost any test setup for embedded systems. As soon as the number of devices to be tested grows, a test farm is inevitable to ensure quality. A test farm with J-Links and the J-Link Test Farm Power Adapter may consist of multiple test devices of the same type or be completely different. We have described a couple of test cases below.
Communication tests
Communication reliability can only be tested with a massive test setups that generates a huge amount of traffic on the communication channel. Specifically wireless traffic using protocols such as WiFi, ZigBee or Matter is prone to interference and requires thorough testing in order to ensure operation even under bad conditions. Communication test setups therefore use heterogenous targets to ensure interoperability with different devices as well as a huge number of similar devices to prove reliability.
Compatibility tests
Testing compatibility of an updated firmware module running on different platforms or of a compiler requires a setup using different devices. A test farm shortens test time by addressing the tests in parallel on multiple different targets and ensures, that any changes to the compiler or firmware module are tested thoroughly against all possible target devices.
Hardware specifications
Pins and connection
The Test Farm Power Adapter has a standard 20-pin 0.1″ socket towards the J-Link and a standard 20-pin 0.1″ header on the target side. It can directly be inserted between the J-Link and the debug cable maintaining a 1:1 connection of all debug signals except pin 19 which carries the target supply.
The adapter also has 2 USB connectors.
Power source and delivery
Power is delivered to the target through a USB-A host connector (USB2.0, power-only). The power source can be either the J-Link debug probe or an USB power source like a hub or wall adapter. In the first case the output voltage coming from J-Link is boosted to 5 V and is limited to around 250 mA. If the Micro USB connector of the Test Farm Power Adapter is used together with an external supply currents of 1 A and more are possible.